In the cradle of Western civilization, ancient Greece was a vibrant culture that made significant contributions to art, architecture, philosophy, and science. One aspect of ancient Greek culture that is often overlooked is their approach to color. While we often think of ancient Greece in terms of marble statues and columns, the ancient Greeks were actually known for their bold and vibrant use of color. In fact, the ancient Greeks recognized seven distinct colors, each with its own unique properties and associations.
The Colors of Ancient Greece

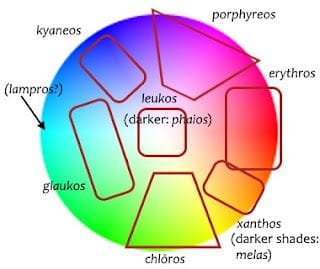
The seven colors of ancient Greece were:
Melas (black) Leukos (white) Erythros (red) Xanthos (yellow) Chloros (green) Cyanos (blue) Porphyra (purple)
Each of these colors had its own unique symbolism and associations. For example, melas (black) was associated with death and mourning, while leukos (white) was associated with purity and innocence. Erythros (red) was associated with passion and energy, while xanthos (yellow) was associated with sunshine and optimism.
The Significance of Color in Ancient Greece

In ancient Greece, color was not just a matter of aesthetics; it was also deeply symbolic and meaningful. Colors were used to convey complex ideas and emotions, and to create a sense of atmosphere and mood. For example, the use of bright, bold colors was often used to convey a sense of energy and vitality, while the use of muted, subdued colors was often used to convey a sense of calm and serenity.
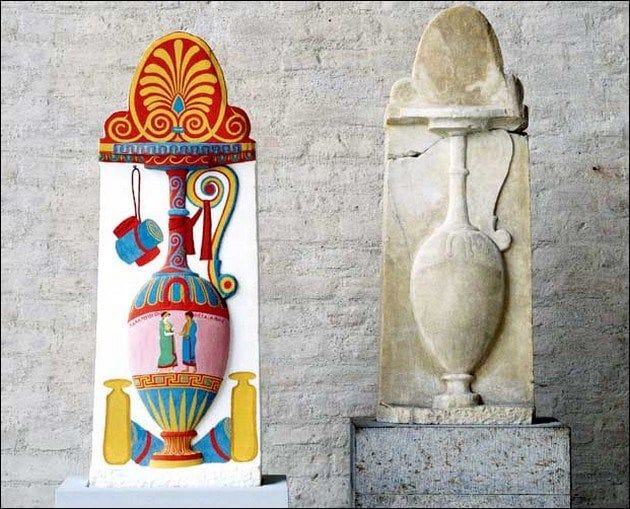
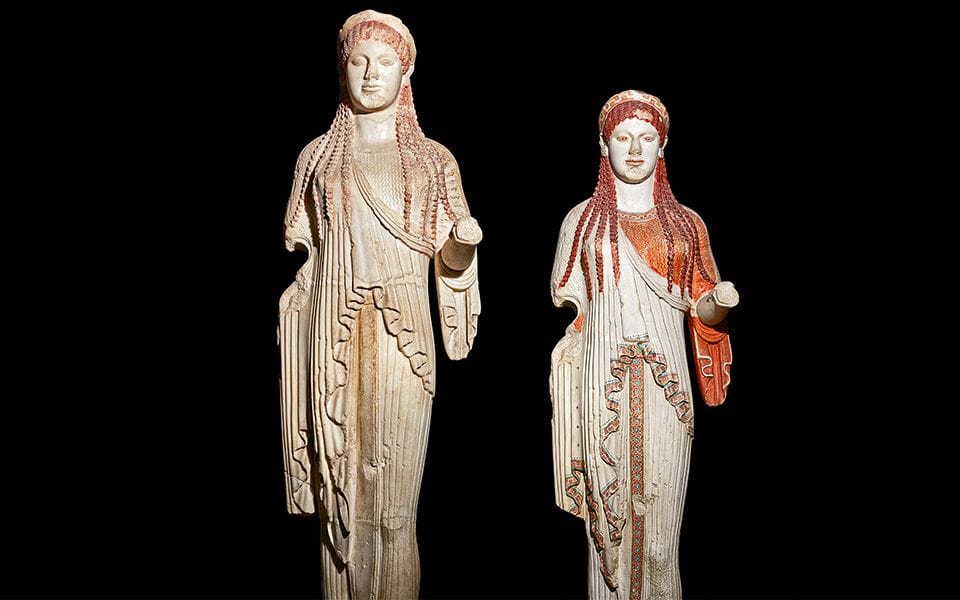
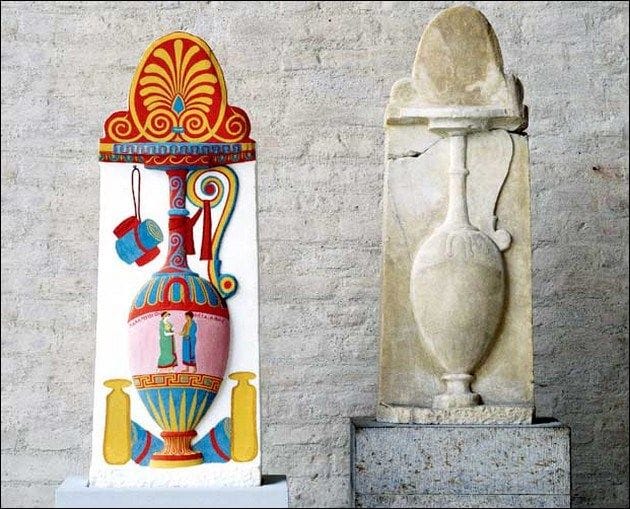
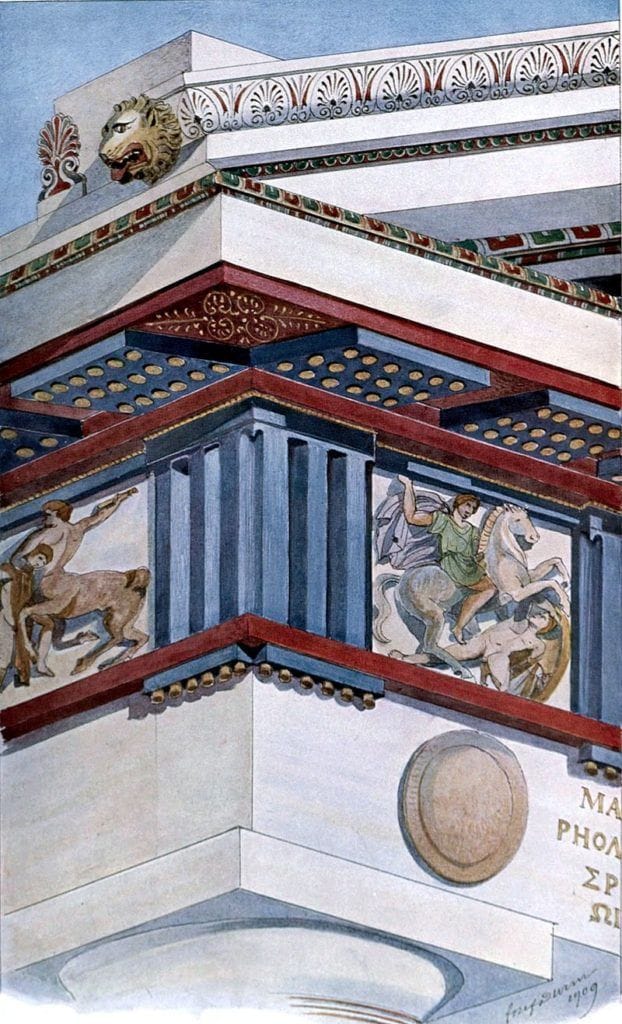
In addition to its symbolic significance, color was also an important aspect of ancient Greek art and architecture. The use of color was carefully planned and executed, with different colors used to create a sense of balance and harmony. For example, the famous Parthenon in Athens features a bold and vibrant use of color, with bright reds and blues used to create a sense of energy and vitality.
The Philosophy of Color in Ancient Greece

In ancient Greece, the philosophy of color was deeply tied to the concept of the four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. Each element was associated with a particular color, with earth associated with black, air associated with white, fire associated with red, and water associated with blue. This philosophy of color was used to explain a wide range of natural phenomena, from the changing colors of the seasons to the colors of the sky and sea.
The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle wrote extensively on the philosophy of color, arguing that colors were not just subjective experiences, but rather objective properties of the physical world. According to Aristotle, colors were caused by the interaction of light and matter, and were an essential part of our experience of the world.
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Color Theory
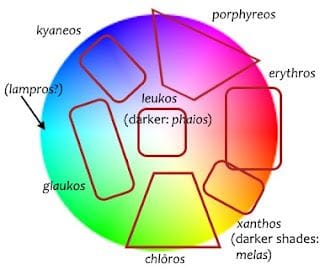
The legacy of ancient Greek color theory can be seen in a wide range of fields, from art and architecture to design and fashion. The use of bold, vibrant colors and the emphasis on balance and harmony can be seen in everything from ancient Greek pottery to modern graphic design.
In addition to its influence on art and design, ancient Greek color theory has also had a profound impact on our understanding of the physical world. The idea that colors are caused by the interaction of light and matter, for example, is a fundamental principle of modern physics.
In conclusion, the seven colors of ancient Greece were a fundamental part of their culture and philosophy. From the symbolic significance of color to the philosophy of color and its legacy, the ancient Greeks made significant contributions to our understanding of color and its role in the world.
What were the seven colors of ancient Greece?
+The seven colors of ancient Greece were melas (black), leukos (white), erythros (red), xanthos (yellow), chloros (green), cyanos (blue), and porphyra (purple).
What was the significance of color in ancient Greece?
+Color was deeply symbolic and meaningful in ancient Greece, and was used to convey complex ideas and emotions. Colors were also carefully planned and executed in art and architecture to create a sense of balance and harmony.
How did ancient Greek color theory influence modern art and design?
+Ancient Greek color theory has had a profound impact on modern art and design, with the use of bold, vibrant colors and the emphasis on balance and harmony continuing to influence artists and designers today.
Gallery of 7 Colors Of Ancient Greece